Posts Tagged ‘I-9/E-Verify News’
Sunday, August 9th, 2015
 We’re starting to intake alot of questions concerning these cards as they now filter through the system to employers charged with handling Form I-9 employment verification.
We’re starting to intake alot of questions concerning these cards as they now filter through the system to employers charged with handling Form I-9 employment verification.
Twelve states and the District of Columbia enacted laws to allow unauthorized immigrants to obtain a driver’s licenses. These states—California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Illinois, Maryland, New Mexico, Nevada, Utah, Vermont and Washington—issue a license if an applicant provides certain documentation, such as a foreign birth certificate, a foreign passport, or a consular card and evidence of current residency in the state. Eight of these states extended driving privileges in 2013. In 2015, Delaware and Hawaii enacted legislation to give unauthorized immigrants driving privileges.
Here are examples of some of the cards with various different annotations.
An employer is required to accept as a list B document an unexpired driver’s license or ID that meets the standard for I-9 purposes. What’s the standard? A photo and other identifying information such as, their name, date of birth, gender, height, eye color and address. The underlying issue here is state law vs. immigration (federal law) and USCIS regulations concerning Form I-9.
Both USCIS and OSC concur, despite the various different types of annotations that appear on driver authorization cards, that they meet the regulations for an acceptable List B document if they adhere to the standards mentioned above.
An employer is required to examine the documents presented by its employee and determine whether they meet Form I-9 requirements. If the employer accepts any document, including a state-issued license or driver authorization card, or other type of ID with a limiting notation as a List B document, the employer must also examine a List C document that evidences employment authorization in order to make a proper determination if the individual is eligible for employment.
Employers may reject a document if it does not reasonably appear to be genuine or to relate to the employee. Rejecting a document that satisfies Form I-9 requirements may constitute illegal discrimination under the Immigration and Nationality Act’s anti-discrimination provision or Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964.
USCIS has published a set of
FAQs on this topic that contain critical information and should be read, discussed and made a part of your training program for those charged with processing I-9 forms. Should you have any questions on this matter or any other concerns regarding employer compliance issues, please feel free to contact us at
info@immigrationcompliancegroup.com or call
562 612.3996.
Tags: Driver Authorization Cards, Driver's License, Employer Compliance, I-9 Form, I-9/E-Verify News, ID Cards, ID Cards for Undocumented Immigrants, Immigration News, Legal Workforce, List B Documents
Posted in Employer Compliance, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, OSC, Social Security, USCIS | Comments Off on Can Driver Authorization Cards be used as a List B Document for I-9 Employment Verification?
Friday, July 17th, 2015

USCIS released details of proposed new changes to the E-Verify program on June 8, 2015 that were published this week. The notice, found here, proposes several changes to E-Verify and seeks public comments until August 7, 2015 and links to new Q&A. These changes will affect all employer users, including Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) contractors.
The three critical changes entail:
1) Requirement that employers re-verify the continuing work authorization of employees within three “Employer” days of the expiration of the employee’s “last” grant of work authorization.
a) This requirement tracks the current continuing duty of employers to re-verify expiring work authorization of employees in Section 3 of the I-9 form or, in the alternative, to complete a new I-9.
b) This differs from the I-9 process in that the E-Verify time frame for re-verification of the employment authorization is three days after its expiration, whereby the I-9 regulations state that an employer re-verify the expiring work authorization of an employee on or before the day it expires. In E-Verify, the proposed process cannot be started until after the expiration of the employment authorization.
c) The re-verification requirement extends to employees hired before an employer began participating in the E-Verify program. Thus, the proposed change would require that employers re-verify an employee’s expiring work authorization regardless of whether they have previously created an E-Verify case for that employee or not. This again differs from the current E-Verify program rules that explicitly prohibit an employer verifying the work authorization of employees hired before the employer began participating in the program (with the exception of FAR E-Verify employers).
2) Requirement that employers print the re-verification confirmation page and retain it along with an employee’s I-9 records or record the E-Verify re-verification case number on the employee’s I-9 Form.
3) Provides a process for employees to seek review of E-Verify Final-Nonconfirmations.
::::::::
Immigration Compliance Group provides US inbound visa services to individuals and employers throughout the USA and abroad. We specialize in business immigration and have a depth of experience in the IT, healthcare, arts, entertainment and sports industries, amongst others. Our services include complex business visas for investors, multinational managers, skilled professionals, outstanding individuals of high achievement and PERM Labor Certification. We additionally provide employer compliance consulting services on proper I-9 (Employment Eligibility Verification) management, auditing, training, and work with our clients to develop a culture of immigration compliance.
Tags: Agriculture, E-Verify, Employer Compliance, FAR E-Verify, Federal Contractors, I-9 Compliance, I-9 Form, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, Legal Workforce, OSC, Seasonal Workers, USCIS
Posted in Agriculture, Employer Compliance, Federal Contractors, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, OSC, USCIS | Comments Off on E-Verify Announces Major Proposed Changes
Saturday, June 20th, 2015
 Since early 2015, qualified California residents have been able to apply for and receive a driver’s license issued by the Department of Motor Vehicles without proving that their presence in the United States is authorized under federal law. All employers must accept the AB 60 driver’s license as a Form I-9 List B Identity document if the license reasonably appears to be genuine and to relate to the individual. As with all permissible List B driver’s licenses, the AB 60 driver’s license must contain either a photograph or list the individual’s name, date of birth, gender, height, eye color, and address. The AB 60 driver’s license only documents the employee’s identity; California employers must still examine a List C document that establishes employment authorization, such as a Social Security card or birth certificate.
Since early 2015, qualified California residents have been able to apply for and receive a driver’s license issued by the Department of Motor Vehicles without proving that their presence in the United States is authorized under federal law. All employers must accept the AB 60 driver’s license as a Form I-9 List B Identity document if the license reasonably appears to be genuine and to relate to the individual. As with all permissible List B driver’s licenses, the AB 60 driver’s license must contain either a photograph or list the individual’s name, date of birth, gender, height, eye color, and address. The AB 60 driver’s license only documents the employee’s identity; California employers must still examine a List C document that establishes employment authorization, such as a Social Security card or birth certificate.
View the Example of the AB-CA Driver’s License annotated with “Federal Benefits Apply”.
Tags: CA AB-60 Driver's License, DACA, Department Of Homeland Security (DHS), Employer Compliance, EMPLOYMENT ELIGIBILITY, I-9 Form, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, Legal Workforce, OSC, Social Security, USCIS
Posted in DACA | DAPA, Employer Compliance, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration Legislation, Immigration News, OSC, Social Security, USCIS | Comments Off on California New AB 60 Driver’s License: Is it Good for Employment Eligibility?
Friday, November 29th, 2013
 On December 8, 2013 E-Verify will release new and revised Memorandums of Understanding (MOUs) that are tailored to each access method.
On December 8, 2013 E-Verify will release new and revised Memorandums of Understanding (MOUs) that are tailored to each access method.
The changes were made in response to customer feedback and to update the MOUs with policy and process changes. Users will find that the new versions have more plain language and are easier to understand, with new titles that clearly identify the access method to which the MOU applies, and bullets that have been changed to letters and numbers to make searching and citation easier. Also, the lengthy sections have been broken up.
Please take the time to review and become familiar with the new MOU’s that apply to your access method; refer to the Fact Sheet and the preview of the new MOUs here. You can also access this information under “View Essential Resources” by logging into E-Verify to review the new and revised MOUs.
What you need to know
- Current E-Verify users will not be required to execute a new MOU, but are bound by any and all enhancements to the E-Verify program including the new or revised MOUs that apply to their access method. Current users should become familiar with the new or revised MOU that applies to them. The effective date of the MOU for existing users is January 8, 2014.
- The E-Verify enrollment process has not changed. New Users will review and execute the new or revised version of the MOU that applies to their access method during enrollment. The effective date of the MOU for new users is December 8, 2013.
- The new and revised MOUs include several updated provisions such as enhanced privacy protections and instructions for reporting privacy and security breaches.
Revised Memorandums of Understanding
TeleConferences
Two teleconferences will be hosted by USCIS to introduce and discuss the revisions schedule as follows:
1) For General Audience: December 11(Wed.) 2:30 – 3:30 EST. Will discuss the revisions made to the existing MOU’s and will open up for Questions. Register here
2) For E-Verify Users: December 12 (Thurs.), 2:30 – 3:30 EST. USCIS officials will provide an overview of the three new MOUs for Web service participants, and be available to answer questions. Register here
If you have any questions regarding the registration process, or if you have not received confirmation email within two business days, please email us at Public.Engagement@uscis.dhs.gov.
Tags: Department Of Homeland Security (DHS), E-Verify, E-Verify MOU, Employment Eligibility Verification, I-9 Form, I-9/E-Verify News, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, Legal Workforce, SSA, USCIS
Posted in Employer Compliance, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, Social Security, USCIS | Comments Off on E-Verify Update —–New/Revised MOU’s Released
Tuesday, September 24th, 2013

The question of whether “N/A” may or must be entered in non-applicable fields, or whether N/A is sometimes required and sometimes optional – is a question we’ve all been wondering about. Here’s recent guidance on the topic . . .
If the passport number and country of issuance fields in Section 1 do not apply, the employee MUST write “N/A.” If all else fails, follow the instructions!…In essence that’s the recent guidance – read the instructions when determining if an N/A response is required as it states when an employer or employee may use N/A or must use N/A. Failing to provide a response in a required field may be considered a verification violattion (yes, it’s true!).
Not to belabor it, but this is another very good reason for providing the instructions to the employees when they are filling out Section 1 and deciding which documents to present in the I-9 process. It would be advisable for the employer representative to also have a copy of the instructions on their desk
The I-9 Instructions: http://www.uscis.gov/files/form/i-9.pdf
How have you been dealing with the “N/A” requirement so far? No judgements – let us hear from you.
Tags: Department Of Homeland Security (DHS), I-9 Audits, I-9 Form N/A requirement, I-9 Training, I-9 Violations, I-9/E-Verify News, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, Legal Workforce, OSC, SSA, USCIS
Posted in Employer Compliance, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration Legislation, Immigration News, OSC, USCIS | Comments Off on Part II — Our Continuing Saga of USCIS Answers Concerning the New I-9 Form
Thursday, September 19th, 2013
 Wall Street Journal (09/12/13) Article Reprinted in Staffing Today
Wall Street Journal (09/12/13) Article Reprinted in Staffing Today
“U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement has notified 1,000 companies across the country that they must submit employment verification documents for audits. This is the largest audit since July 2009. The audits target restaurants, food processors, high-tech manufacturers, the agriculture sector, and other industries that cumulatively employ tens of thousands of workers.
The audits will not lead to deportation of illegal workers, but those workers will lose their jobs, which critics point out can drive immigrants to exploitative, off-the-books work. They can also cause lost productivity and result in large fines and the loss of employees to competitors. ICE typically requests Forms I-9, worker rosters, and payroll stubs, then issues notices of suspect documents to employers, which inform their workers they must either produce legal documentation or quit. More than 10,000 employers have been audited in the past four years. The audits have grown more intense, and ICE now requests not just basic paperwork but weekly work schedules, names of managers, lists of temporary staffing firms used, and the company’s articles of incorporation.”
This is certainly NOT what you want to take place in your company. If you know that you are overdue for an I–9 audit (whether full or partial), or require additional training or should have your policies and procedures examined in light of recommended best practices, being proactive will always be your best defense. So, do not procrastinate. We’d be glad to work with you toward this end. You contact us at info@immigrationcompliancegroup.com or by calling 562 612.3996.
Reprint here: http://staffingtoday.net/2013/09/13/
Tags: Employer Crackdown, Employer I-9 Audits, I-9 AUDIT, I-9 Fines, I-9 Training, I-9 Violations, I-9/E-Verify News, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE I-9 Audit, Illegal Workers, Immigration News, Legal Workforce, Undocumented Workers, USCIS
Posted in Uncategorized | Comments Off on U.S. Begins New Crackdown on Hiring Illegal Workers
Monday, September 9th, 2013

USCIS has gone ‘live’ day with a new TNC communication process. The highlight of the latest enhancement is the combining of the TNC Notice and Referral Letter into one document – the Further Action Notice.
The Further Action Notice simplifies the TNC communication process by combining the employee’s biographical information, the reason for the TNC, the employee’s decision to contest, and employee instructions for contesting a TNC into a single document. There will also be fewer screens to click through.
Here is a chart that provides the action that needs to be taken in various different TNC scenarios — very helpful, as well as a Further Action Notice sample, and a new email notification that will be sent to employees when their cases are referred to SSA or DHS.
Tags: Department Of Homeland Security (DHS), E-Verify Employee Email, E-Verify Further Action Notice, E-Verify TNC Enhancement, I-9, I-9 Compiance, I-9/E-Verify, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, Legal Workforce, SSA, USCIS
Posted in Department Of Homeland Security (DHS), Employer Compliance, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, Social Security, USCIS | Comments Off on E-Verify Releases New TNC Enhancements
Tuesday, May 7th, 2013
 USCIS Will not Accept Previous Versions of Form I-9 as of May 7, 2013
USCIS Will not Accept Previous Versions of Form I-9 as of May 7, 2013
USCIS reminds employers that beginning today, May 7, 2013, they must use the revised Form I-9, Employment Eligibility Verification (Revision 03/08/13)N for all new hires and reverifications. All employers are required to complete and retain a Form I-9 for each employee hired to work in the United States.
The revision date of the new Form I-9 is printed on the lower left corner of the form. Employers should not complete a new Form I-9 for existing employees, however, if a properly completed Form I-9 is already on file.
A Spanish version of Form I-9 (revision 03/08/13)N is available on the USCIS website for use in Puerto Rico only. Spanish-speaking employers and employees in the 50 states, Washington, D.C., and other U.S. territories may use the Spanish version for reference, but must complete and retain the English version of the form.
The revised forms are available online at www.uscis.gov/I-9. USCIS has also offering free webinars to help employers learn about the new form. To order forms, call USCIS toll-free at 1-800-870-3676. For free downloadable forms and information on USCIS programs, immigration laws, regulations, and procedures, please visit www.uscis.gov and go to the ‘forms’ menu or I-9 Central
Tags: Employment Eligibility Verification, I-9/E-Verify News, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration Compliance Group, Immigration News, Immigration Reform, Legal Workforce, M-274 Employer Handbook, New I-9 Form, Social Security
Posted in Employer Compliance, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration Legislation, Immigration News, Social Security | Comments Off on Employers Must Use Revised Form I-9, Employment Eligibility Verification Form
Thursday, August 16th, 2012
The Department of Justice Office of Public Affairs recently published a press release pertaining to the employment of two refugees resolving allegations that the company discriminated under the anti-discrimination provision of the Immigration and Nationality Act (INA), when it impermissibly delayed the start date of two refugees after requiring them to provide specific Form I-9 documentation. Best Packing’s violations occurred when they required the refugees to supply the company with additional Form I-9 verification documents in excess of the law. The claim alleged that other non-refugee employees were not required to supply documents other than state issued licenses and social security cards.
In two charges filed with the department, the refugees alleged that they were not allowed to begin employment until they produced unexpired, Department of Homeland Security-issued employment authorization documents, despite the fact that they initially presented sufficient documentation for employment eligibility verification purposes. The charging parties had presented unexpired state identification cards and unrestricted Social Security cards. The state ID’s and unrestricted SS cards were deemed insufficient proof of work authorization.
It is necessary for all those charged with Form I-9 processing at your organization to be very familiar with the list of acceptable documents and to have a thorough understanding of the fact that each employee has the right to present a list A document or a combination B plus C document as long as they are acceptable documents, appear to be genuine and represent the employee that is before you.
Under the settlement agreement, Best Packing agreed to pay $4,379 in back pay and comply with all the requirements of the INA. Understanding the Form I-9 requirements for verifying refugee/asylee(s) will prevent your company from falling victim to similar discriminatory hiring practices.
The process by which an employer is required to verify the employment eligibility of a refugee/asylee(s) when presented with documentation other than the above-referenced List B plus List C combination, can be a bit complicated. Let’s review this.
Asylees and Refugees are individuals seeking the protection of the United States due to persecution suffered in the home country based upon: race, religion, nationality, social group, or political ideology. These individuals are authorized to work in the US because of their immigration status. When presented with documentation of asylum or refugee status, it is advisable to be aware of the following in regard to examining the I-9 form and the documents presented:
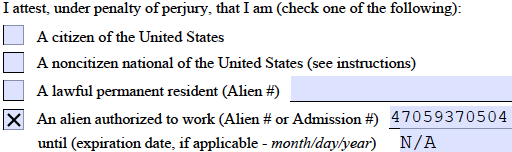
SECTION 1:
- The employee should check the “An alien authorized to work” box
- Write the I-94 or Alien Registration Number in the first space
- Write “N/A” in the second space, because their employment authorization does not expire
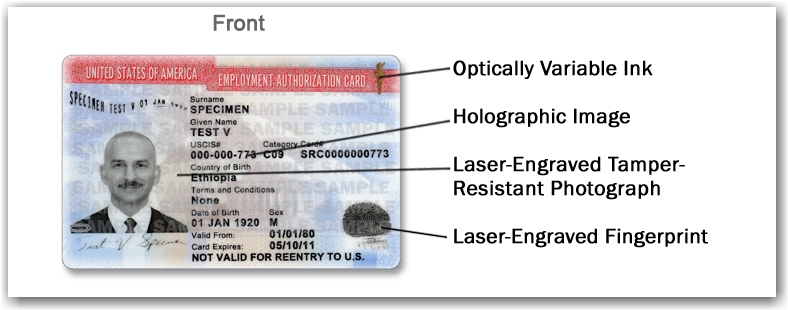
SECTION 2:
Acceptable Documents are I-94, I-766, or their Employment Authorization Document also known as an EAD card
NOTE: this section presents two different scenarios that require strict attention to time restrictions and combinations of required documents to be presented in order to comply with the USCIS regulations. To complete this section choose from the applicable scenarios below:
Scenario One: Refugee presents a Form I-94:
When presented with a Form I-94 containing an unexpired refugee admission stamp, the employer must accept it as a receipt establishing both employment authorization and identity for 90 days. After 90-days, the employee must present either an EAD or a combination of a List B document and List C (an unrestricted social security card.)



Scenario Two: Asylee presents a Form I-94:
An employer must accept Form I-94 or Form I-94A with one of the stamps or notations below indicating asylee status:
- Asylum granted indefinitely
- 8 CFR 274a.12(a)(5)
- INA 208
This is a List C document that does not require/contain an expiration date. However, the asylee will need to present a List B identity document with this Form I-94.
*Decisions from immigration judges granting asylum are not acceptable.

For further assistance on training your company’s hiring personnel on all of the requirements of Form I-9 compliance, contact one of our immigration professionals at info@immigrationcompliancegroup.com or call 562 612.3996.
Tags: Best Packaging I-9 Ruling, DOJ, I-9 Acceptable Documents, I-9 Anti-Discrimination Provision, I-9 Discrimination, I-9 Document Examination, I-9 for Refugees/Asylees, I-9 Over-Documentation, I-9 Training, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, OSC, Worksite Enforcement
Posted in Employer Compliance, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, Uncategorized, USCIS | Comments Off on Form I-9 How To Guide: Employing Refugee/Asylee(s)
Thursday, May 17th, 2012
By: Timothy Sutton, Communications Editor
The Hamilton Project, at the Brookings Institution held a forum on U.S. immigration on May 15, 2012. US Davis Economist,  Giovanni Peri, purposed a radical overhaul to the entire immigration system. In short, Peri proposed a national auction system wherein employers bid for employee visas and proceeds of these sales fund local healthcare and education. The auction prices would be set with a reserve to ensure a minimal guaranteed income stream. Uncapped, the market would dictate the number of visas issued annually. This proposal seems to find a common ground between business needs and government regulation, benefiting the low-skilled labor market.
Giovanni Peri, purposed a radical overhaul to the entire immigration system. In short, Peri proposed a national auction system wherein employers bid for employee visas and proceeds of these sales fund local healthcare and education. The auction prices would be set with a reserve to ensure a minimal guaranteed income stream. Uncapped, the market would dictate the number of visas issued annually. This proposal seems to find a common ground between business needs and government regulation, benefiting the low-skilled labor market.
Auctioning low-skilled labor visas should help reduce the population of roughly 11.5 million illegal immigrants. Employers will be able to hire a legal workforce up to the point where auction prices for visas offset low wage savings. At that time, I-9 audits and workplace raids should continue to deter further hiring of illegal immigrants. This larger, stable and legal temporary workforce will help stabilize the economy. Changes are welcomed for companies like 3M that recently experienced a “brain drain.” 3M has been outsourcing science and technology jobs to Asia, citing the instability of the low skilled labor market they rely on to support their laboratories, manufacturing, research and development.
While Peri’s proposals are likely years away from actually being introduced into legislation, public officials like Senator John Cornyn continue to push for business friendly immigration. Senator Cornyn recently introduced legislation that would add 85,000 H-1B temporary visas issued annually to foreign-born engineers, mathematicians, scientists and other high-tech workers. Cornyn reminded the Senate, “We have to remember how this country was built. All of us are sons and daughters of immigrants that showed up here and made our way. We’ve cut off that flow.”
For continued coverage of proposed immigration reform and legislation, as well as the latest developments in immigration politics, subscribe to our blog and immigration and I-9 newsletters here.
Interested in staying current with I-9/E-Verify news and issues? Check out our group on LinkedIn.
Tags: Brookings Institute, H-1B Quota, H-1B Visas, I-9 Form, I-9/E-Verify News, I-9/E-Verify News, Immigration Compliance Group, Immigration Legislation, Immigration News, Immigration Politics, Immigration Reform, Legal Workforce, Senator Cronyn, Skilled Workers
Posted in H-1B Visas, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration Legislation, Immigration News, USCIS | Comments Off on Immigration Reform: The Future Of Immigration Policy…Visa Auctions?
 We’re starting to intake alot of questions concerning these cards as they now filter through the system to employers charged with handling Form I-9 employment verification.
We’re starting to intake alot of questions concerning these cards as they now filter through the system to employers charged with handling Form I-9 employment verification.